
Vinylon
Vinylon is polyvinyl acetal fiber The product name is also called Vinylon abbreviation, English Vinylon or Vinalon. Its performance is close to that of cotton, and it is known as “synthetic cotton”. It is the most hygroscopic variety among existing synthetic fibers. There are fewer pure fibers, and they are mostly blended or interwoven with other fibers.
The development of vinylon
Vinyllon was made in Germany in the 1930s, but it is not resistant to hot water and is mainly used for surgical sutures. In 1939, the heat treatment and acetalization methods were successfully researched, making it a fiber with good resistance to hot water. The raw materials for producing vinylon are easily available, the manufacturing cost is low, and the fiber strength is good. In addition to being used in clothing, it also has a variety of industrial uses. However, due to its long industrial production process, the comprehensive fiber performance is not as good as polyester, nylon and acrylic fiber, and the annual output is small, ranking fifth among synthetic fiber varieties.
Production of vinylon
The main component of vinylon is polyvinyl alcohol, but vinyl alcohol is unstable. It is generally polymerized with stable vinyl alcohol acetate (i.e. vinyl acetate) as a monomer. The generated polyvinyl acetate is then hydrolyzed to obtain polyvinyl alcohol, which is then treated with formaldehyde after spinning to introduce a six-membered ring structure into the polymer chain to generate polyvinyl formal to enhance its strength. Only in this way can you get vinylon that is resistant to hot water.
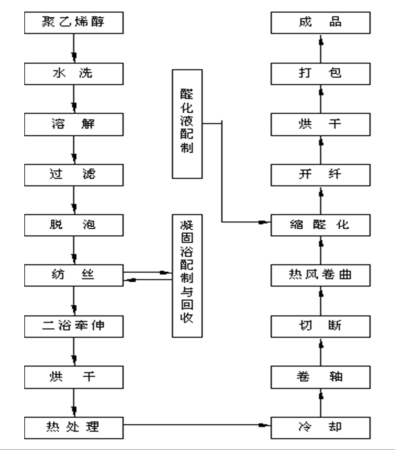
- Before decomposition, polyvinyl alcohol has no obvious molten state, so The solution spinning method is used, and wet spinning using water as the solvent is often used. The preparation process of polyvinyl acetalized fiber includes the preparation of spinning solution, spinning and finishing
- Preparation process
Preparation of spinning solution: Dissolve washed and refined polyvinyl alcohol in hot water of 80~90℃ to make a concentration of 15%~16% of spinning solution.
Spinning: The spinning liquid is pressed out from the spinneret and solidified into fibers in the coagulation bath. Coagulants commonly use ammonium sulfate and other electrolyte solutions with strong dehydration capabilities.
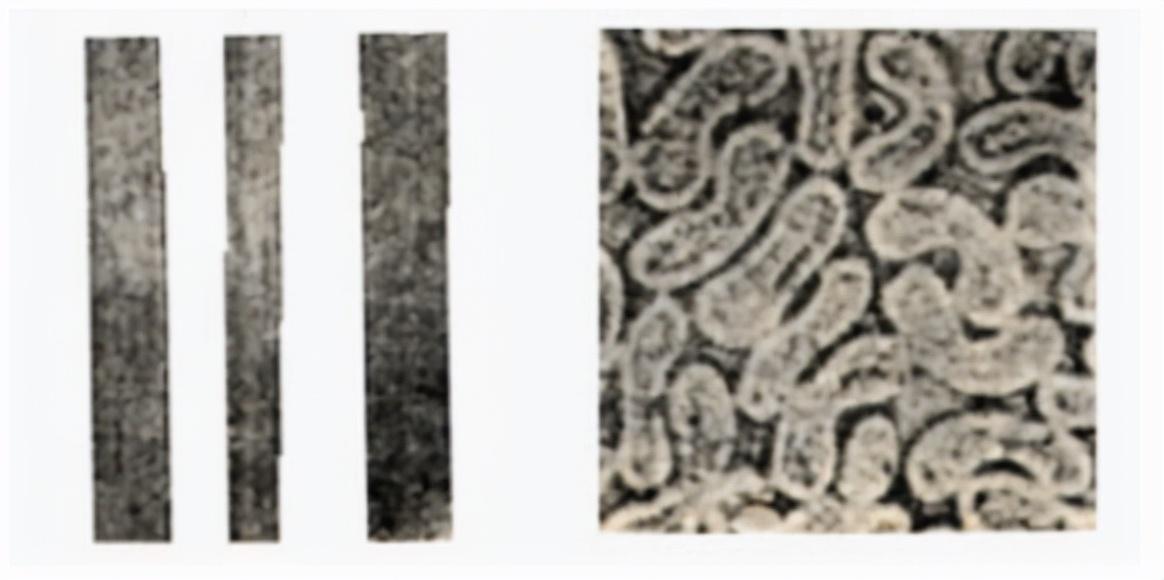
The morphological structure of vinylon
Longitudinal straight, with 1~2 grooves,
The cross-section is kidney-shaped and has an obvious skin-core structure.

Characteristics of vinylon
1) Hygroscopicity: good (WK=5%), good sweat absorption and moisture permeability.
2) Warmth retention: better than cotton. Similar to wool, it is easy to wear as winter clothes.
3) Strength: The wear resistance is better than cotton. But less flexible.
4) Dyeability: poor, can only dye dark colors.
5) Acid and alkali resistance: good chemical stability, resistant to acid, alkali, oil, etc. No mass change occurs in solution.
6) The hot water resistance is not good enough, the elasticity is poor, and the dyeability is poor.
Identification
It is not easy to ignite. It melts and shrinks near the flame. There is a little flame at the top when burning. When the fibers are melted into a gel, the flame becomes larger. There is thick black smoke and a bitter smell. It burns Small black bead-like particles remain, which can be crushed with your fingers.
Dyeing process of vinylon
Vilon is difficult to dye into dark colors, and the dyeing color is darker and prone to “white core” phenomenon. There are hydrophilic hydroxyl groups and hydrophobic acetal groups on the macromolecules of vinylon fiber, so it has varying degrees of affinity for most dyes. If the dyes can be screened during dyeing, and a variety of dyes can be dyed in one or two baths in the same bath, the white core phenomenon can be overcome and deep colors can be obtained.
The following is a brief introduction to the application of different dyes in vinylon dyeing.
① Choose direct dyes with fewer sulfonic acid groups and more amino groups in the molecular structure. Because the former has high water solubility and low directivity, while the latter is just the opposite. Practice has proved that when dyeing vinylon with direct dyes, the dosage should generally be controlled at around 1% (owf).The main varieties of polyester fabrics are
1) Vitamin/Viscose Gabardine
Also known as Viscose/Viscose Dongfeng, it is a yarn blended with 50% vinylon and 50% wool-type viscose fiber. Woven by a 2/2 twill weave, it has the same front and back sides. The texture is thick and tight, tough, durable, and has characteristics similar to wool gabardine but with a better luster than wool. It is suitable for coats
2) Divin/Validine
Using vinylon and wool-type viscose for plain weaving, the obtained Veridin-style fabric is usually woven with a vinylon/artificial wool ratio of 70/30 or 50/50, which is thick and durable. Or tight and thin, the disadvantages are large shrinkage and poor heat resistance. Mostly used as mid-to-low-end summer clothing.
Vinyl cement cable tube
As a new generation of high-tech pipes, vinylon cement cable pipes are not used in many fields, but they are highly adaptable. There are five typical application areas. Category: (1) Urban power grid construction and renovation projects. (2) Urban municipal reconstruction projects. (3) Civil aviation airport project construction. (4) Industrial park and community project construction. (5) Traffic road and bridge engineering construction.
Vinyl cement cable pipe has become the leader in the laying of some national-level buildings. The cable tube eliminates the traditional cement protective tube and adds more protective vinylon. The fusion of the two can make the cable protection better
Water-soluble vinylon filament is widely favored
Vinyl fiber is a valuable functional differentiated fiber, and water-soluble vinylon fiber is a special variety of vinylon. It is divided into two categories: filament and short fiber. Water-soluble filament is the ideal water-soluble fiber. fiber. Water-soluble dimensional filament not only has an ideal water-soluble temperature and strong elongation, which can range from 0 to 100°C, but also has good acid and alkali resistance and dry heat resistance. When dissolved in water, it is odorless and non-toxic, and the aqueous solution is non-toxic. The transparent color can be naturally biodegraded in a short period of time








