1. Commonly used basic concepts of chemical fibers
1. Fiber (fibre)

Fiber is a relatively flexible, thin and long substance, with an aspect ratio generally greater than 1000:1. Typical textile fibers have a diameter of several microns to tens of microns, a length of more than 25mm, and a linear density of the order of 10 to the negative fifth power g/mm.
For textile fibers, there is also a larger Elongation at break. The typical elongation at break of textile fibers ranges from 10% to 50%.
2. Filament (continuous filament)

In the chemical fiber manufacturing process, we get Fibers whose length is measured in kilometers are called filaments. Filament includes monofilament, multifilament and cord yarn.
① Monofilament is a continuous single fiber spun with a single-hole spinneret.
②Multifilament is a filament composed of dozens of monofilaments.
③Cord yarns are composed of more than a hundred to hundreds of single fibers and are used to make the threads of tire cord fabrics.
3. Tow

The filament bundles range from tens of thousands to hundreds Thousands of monofilaments are gathered into a bundle and used to cut into short fibers, or are drawn and cut into slivers (tops), which are also called drawn-cut fibers (equivalent to roving slivers on cotton spinning).
4. Short fiber (staple)
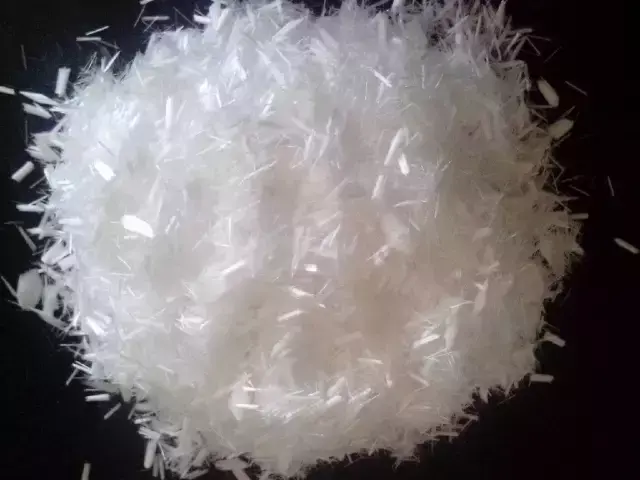

Chemical fiber products are cut into several centimeters To a length of more than ten centimeters, fibers of this length are called short fibers. According to the different cutting lengths, short fibers can be divided into cotton type, wool type, and medium and long type short fibers.
① Cotton short fiber has a length of 25 to 38 mm and a thin fiber (linear density of 1.3 to 1.7 dtex), similar to cotton. It is mainly used for polyester-cotton fabrics blended with cotton.
②Wool-type short fiber has a length of 70~150mm, thick fiber (linear density 3.3~7.7dtex), similar to wool, and is mainly used for blending with wool – wool-polyester fabrics.
③Medium-length short fiber The fiber length is 51~76mm, and the linear density of the fiber is between cotton type and wool type (2.2~3.3dtex). It is mainly used to make medium-length fiber fabrics.
5. Stretch-broken tow
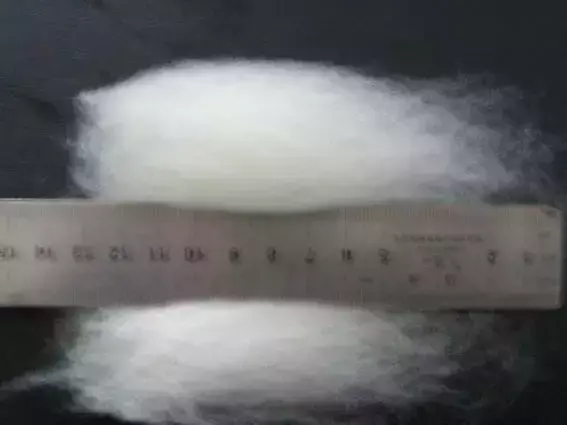

Chemical fiber tow warp Short fibers of unequal length formed by stretching and breaking in the longitudinal direction are also called unequal length short fibers.
6. Shaped fibers
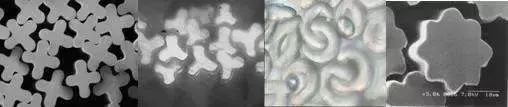
During the synthetic fiber forming process, Fibers or hollow fibers with non-circular cross-sections spun with special-shaped spinnerets (non-circular holes) are called special-shaped cross-section fibers, or special-shaped fibers for short.
Special-shaped fibers have special luster, fluffiness, stain resistance and pilling resistance, and fiber resilience and coverage can also be improved. For example, polyester with a triangular cross-section has glitter; polyester with a five-lobed cross-section has a luster similar to silk, is anti-pilling, has good hand feel and coverage; some hollow fibers also have special uses, such as making reverse osmosis membranes and used in artificial Kidneys, desalination, sewage treatment, hard water softening, etc.
7. Composite fiber
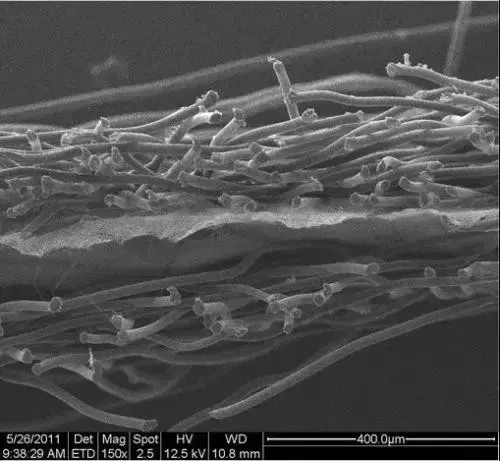

Composite fiber is a combination of two or more Melts or concentrated solutions of more than one type of fiber-forming polymers are fed into the same spinning assembly by taking advantage of differences in components, ratios, viscosity or varieties, and then merge at appropriate parts of the assembly to form fibers in the same spinning hole. Spray out and become a fiber, called composite fiber.
There are many varieties of composite fibers, including side-by-side type, sheath-core type, scattered type (island type), etc.
8. Textured yarn

Textured yarn includes all textured yarns Silk and yarn, such as elastic yarn and bulked yarn, are textured yarns.
Elastic yarn is deformed filament, which can be divided into high-elastic yarn and low-elastic yarn. Elastic yarn has good stretchability and fluffiness, and its fabric is close to wool, silk or cotton fabrics in terms of thickness, weight, opacity, coverage and appearance characteristics.
Bulk yarn uses the thermoplasticity of polymers to mix two synthetic fiber tops with different shrinkage properties in proportion. After heat treatment, the high-shrinkage top forces the low-shrinkage top to curl. This makes it stretchy and fluffy. Textured yarns and bulked yarns similar to wool are mainly acrylic.
9. Superfine fiber

Due to the thickness of the single fiber, the fabric The performance has a great influence, so chemical fibers can also be classified according to the thickness (linear density) of single fibers, generally divided into conventional fibers, fine denier fibers, ultra-fine denier fibers and ultra-fine fibers.
Conventional fiber linear density is 1.4~7dtex.
The linear density of fine denier fiber is 0.55~1.3dtex, which is mainly used for light and medium-thick fabrics like silk.
Superfine fiber has a linear density of 0.11 to 0.55dtex and is mainly used in high-density waterproof and breathable fabrics, artificial leather, imitation peach skin fabrics, etc.
Ultra-fine fiber has a linear density below 0.11dtex and can be produced by island spinning method. It is mainly used in special fields such as artificial leather and medical filter materials.
10. Differential fiber (differential fiber)
Generally refers to edible chemical fibers that innovate conventional chemical fiber varieties or impart certain characteristics through chemical modification or physical deformation.

The modifications in the polymerization and spinning processes include copolymerization, super gloss, super high shrinkage, and metadying , easy to dye, quick to dye, antistatic, anti-pilling, anti-mildew, anti-bacteria, anti-fouling, anti-odor, moisture-absorbent, sweat-absorbent, waterproof, fluorescent discoloration and other fibers.
The products formed in the spinning, stretching and deformation processes include blending, composite, hollow, special-shaped, different shrinkage, different materials, different colors, fine denier, ultra-fine, extra-thick, three-dimensional curl, Network, mixed fiber, hybrid, sheath-core, juxtaposition, bamboo, mixed color, coating, etc. all belong to the category of differentiated fibers.
Differential fibers are mainly used in clothing and clothing fabrics, which can improve economic benefits, optimize processes, save energy, reduce pollution, and increase new textile products.
11. Special fiber
Special fibers generally refer to chemical fibers with special physical and chemical structures, properties and uses, such as high-performance fibers, functional fibers, etc.
Specialty fibers are mainly used in industry and cutting-edge technology fields.
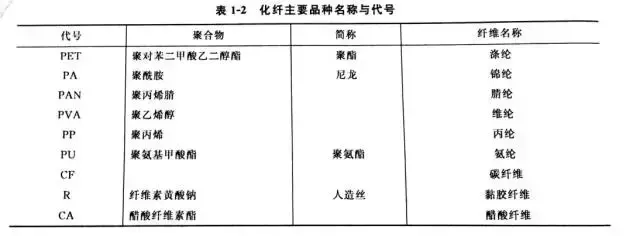
2. Names and codes of the main varieties of chemical fibers
The main varieties of chemical fibers generally have common names and codes, and their fiber-forming polymers usually also have abbreviations. The names and codes of the main varieties of chemical fibers are shown in Table 1 -2.