Modern clothing fabrics, new products are emerging one after another, and the technology is changing with each passing day. But everything remains the same. As long as we master some basic knowledge about fabrics, we can quickly distinguish the advantages and disadvantages of clothing and judge whether it can meet the needs of use. Clothing fabrics are made of fibers through spinning, weaving, dyeing, finishing and other processes. Today we will start from the source and take a look at some basic knowledge about clothing fibers.

What is fiber? That is, fibrous materials that are slender, soft, and have a length much larger than their cross-sectional area are collectively called fibers. Let’s first make the following brief table of the basic classifications of clothing fibers, and then explain them in detail later.
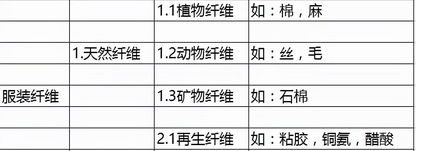
1. Natural fiber
1.1 Plant fiber: from plant stems, roots, fruits, Fiber obtained from fruit husks.
1.1.1 Cotton: Cotton and kapok are common, which are single-cell fibers obtained from plant seeds.
The advantage is that it is skin-friendly and soft, moisture-absorbent and breathable, and has good warmth retention properties. The disadvantage is that it is easy to wrinkle, deform and shrink.
1.1.2 Flax: Commonly found are flax, ramie, etc., which are bast fibers obtained from plant stems.
The advantage is that it has natural luster, good color fastness, UV resistance, mildew resistance, very cool feeling when worn, and does not stick to the body when sweating. The disadvantages are that it feels rough, is less comfortable to wear than cotton, and is easy to shrink and wrinkle.
1.2 Animal fiber: fiber obtained from animal hair or secretions, main component It’s protein.
1.2.1 Silk: Commonly seen are mulberry silk and tussah silk, which are continuous long fibers formed by solidifying the silk liquid secreted by mature silkworms when they spin cocoons. Silk is also the longest natural fiber, reaching more than 10 meters in length.
The advantages are good gloss, softness and smoothness, good hygroscopicity, and a certain nourishing effect on the skin. The disadvantages are poor fastness, easy to snag and rot, easy to generate static electricity, poor anti-bacterial and insect-proof properties, and difficult to take care of.
1.2.2 Hair: Commonly found are wool, rabbit hair, camel hair, yak hair, etc., which are fibers obtained from animal hair.
The advantages are good warmth retention, good elasticity, good hygroscopicity and anti-static. The disadvantages are that it has poor antibacterial and insect-proof properties, is prone to yellowing, pilling and shrinkage, and is difficult to take care of.
1.3 Mineral fiber: Fiber obtained from rock minerals is generally used in industry, so I won’t go into details here.
2. Man-made fiber
2.1 Regenerated fiber: using natural cellulose (bamboo, trees, shrubs, etc.) as raw material , does not change its chemical structure, but only changes the physical structure of natural cellulose, thereby creating regenerated cellulose fibers with better performance.
2.1.1 Viscose fiber: Mainly made from cotton pulp and wood pulp, natural cellulose is separated and regenerated through chemical reactions.
The advantages are good hygroscopicity, antistatic, antibacterial, easy to dye, skin-friendly and soft, hygroscopic and breathable. The disadvantages are poor elasticity, not resistant to washing, easy to wrinkle, poor resilience, heavier weight, and greater production pollution.
2.1.2 Cupro fiber: It is a naturally degradable regenerated fiber extracted from cotton lint.
The advantages are moisture absorption and breathability, antistatic, high strength, silky texture and good drape. The disadvantages are low output, high price, and not acid resistant.
2.1.3 Acetate fiber: Man-made fiber made from acetic acid and cellulose through esterification reaction.
The advantages are moisture absorption, breathability, antistatic, good resilience, soft and smooth, and physical properties close to mulberry silk. The disadvantage is that the price is higher and you need to pay attention to the washing method.
2.2 Chemical fiber: A polymer compound extracted from coal and petroleum, which changes its molecular structure through a series of chemical reactions to obtain usable fibers.
2.2.1 Polyester: also known as polyester fiber.
The advantages are mildew and antibacterial, good wrinkle resistance, strong and durable, high strength and good light resistance. The disadvantages are poor moisture absorption and breathability, easy pilling, and difficult to dye.
2.2.2 Nylon: also known as nylon, polyamide fiber.
The advantages are mildew and antibacterial, good wear resistance, light weight, good elasticity and resilience, and sun resistance. The disadvantages are poor hygroscopicity, easy to wrinkle, and poor heat resistance.
2.2.3 Acrylic fiber: also known as polyacrylonitrile.
The advantages are good elasticity, good warmth retention and high strength. The disadvantages are poor hygroscopicity, poor heat resistance, and no alkali resistance.
2.2.4 Polypropylene: also known as polypropylene fiber.
The advantages are light weight, can float on the water, small thermal conductivity, strong warmth retention, obvious moisture absorption and perspiration effect, and good elasticity. The disadvantages are poor light resistance, easy to age, not resistant to high temperatures, and cannot be ironed.
2.2.5 Spandex: Also known as polyurethane fiber, it is an elastic fiber. Spandex is usually not used alone but is blended with other yarns.
The advantage is flexibilityLarge, good shape retention. The disadvantages are poor performance, poor hygroscopic strength, and easy to break.
The above is today’s content, I hope it will be helpful for you to understand fabrics.






